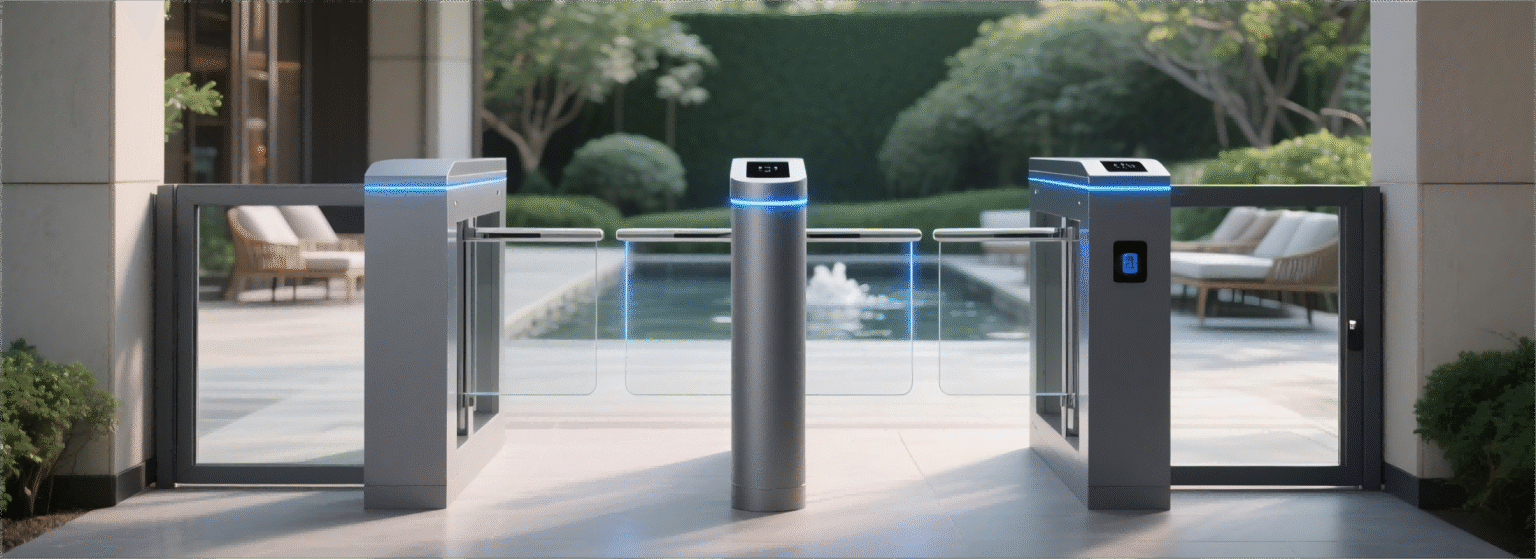
Speed Gate
The Evolution of Speed Gates in Modern Infrastructure
In today’s world, urbanization, security needs, and digital transformation are rising together. Public awareness of access control has grown significantly. Many countries with dense populations and expanding cities recognize the need to balance safety, efficiency, and convenience. This applies to both public and private spaces.
This shift goes beyond preventing unauthorized entry. It reflects society’s demand for secure yet seamless movement. Governments, organizations, and citizens now see access control as a driver of smart cities and sustainable infrastructure.
Market data supports this growing trend. The global access control systems market may surpass USD 15 billion by 2030. Speed gates are among the fastest-growing segments. In Asia-Pacific, mega-cities increasingly deploy them in metros, airports, and offices. In Europe and North America, speed gates integrate with biometrics and visitor systems. This shows their importance in next-generation smart buildings.
Amid these changes, speed gates have become advanced and versatile solutions. They are more than physical barriers, combining technology with intelligent infrastructure. In offices, metros, airports, universities, and government sites, they enable secure, precise, and fast entry. By joining mechanical reliability with digital intelligence, speed gates are transforming urban movement. They improve security, efficiency, data management, and user experience. These strengths make them essential in today’s connected world.
Speed Gates and the Rise of Smart Buildings
The rise of smart buildings is one of the defining features of modern urban development. Today, office towers, government complexes, and mixed-use facilities are no longer designed just for functionality—they are expected to deliver efficiency, sustainability, and seamless user experiences. Speed gates fit directly into this vision, serving as an essential bridge between physical security and digital intelligence.
According to industry reports, the global smart building market is expected to exceed USD 320 billion by 2030. This growth is driven by IoT, AI, and integrated security systems. Within this ecosystem, speed gates play a critical role by linking access control with building management platforms. When connected with HVAC, lighting, and occupancy sensors, they not only control entry but also provide real-time data. This helps facilities optimize energy use, manage crowds, and improve operational planning.
In corporate environments, speed gates are now integrated with HR systems, visitor platforms, and cloud-based dashboards. Employees can access buildings through biometric scans, mobile NFC, or QR codes. This reduces reliance on badges while improving both security and efficiency. Visitors can pre-register with apps and pass smoothly through gates, which simplifies the entire check-in process.
Real-world adoption confirms this trend. Singapore’s Marina Bay Financial Centre uses speed gates with biometric verification and tenant management systems. This improves both security and convenience for daily operations. In the U.S. and Europe, tech campuses are embedding speed gates into workplace ecosystems. They use them not only for security but also for workplace analytics and space utilization.
Speed gates are no longer viewed as simple physical barriers. They are evolving into connected access nodes within smart buildings. With fast throughput, flexible authentication, and useful data insights, they enhance both efficiency and safety. This combination defines the future of modern infrastructure.
Enhancing User Experience
Smarter Authentication Methods
Transition from cards and tickets to biometrics, mobile credentials, and QR codes.Surveys show that over 60% of enterprises now prefer biometric or mobile-based entry solutions, citing convenience and reduced credential theft.With facial recognition, fingerprint, or smartphone tap, users can pass through without carrying physical tokens.

Improved Throughput Efficiency
Biometric-enabled speed gates process 40–50 people per minute, compared to 20–25 people with card-based systems.In high-traffic environments (metro stations, airports, corporate lobbies), this efficiency means:shorter queues、smoother passenger flow
and enhanced daily commuter and visitor satisfaction
Multi-Modal Flexibility
Support for multiple access methods simultaneously: NFC employee badges, QR tickets, mobile apps, and biometrics.
Example: Shanghai Metro integrates transport cards, QR codes, and facial recognition into its speed gates, serving millions of daily riders with maximum convenience.

Accessibility and Inclusivity
Designed with wide passage options for wheelchair users, strollers, or travelers with luggage.Silent motors and elegant finishes improve comfort while blending into modern architectural designs.Enhances not only usability but also a building’s overall image and atmosphere.
Invisible yet Effective Security
By merging security with seamless movement, speed gates make access control feel fast, intuitive, and user-friendly.Instead of feeling restrictive, they provide a nearly invisible layer of protection, boosting both efficiency and satisfaction.

The Role in Public Infrastructure
Public infrastructure, especially airports, metros, and train stations, relies on speed gates for security and efficiency. Millions pass daily, so even small improvements in accuracy or throughput make a big difference.
In metros, speed gates handle heavy passenger flows without slowing verification. Reports show Beijing and Tokyo networks serve over 10 million daily riders. Speed gates enable this scale by linking with tickets, apps, and payment systems. Passengers enter using cards, QR codes, or facial recognition, avoiding manual bottlenecks.
Airports use speed gates for the “seamless travel” initiative. Many international terminals deploy biometric gates for boarding, immigration, and security. At Singapore Changi Airport, facial and iris gates let passengers clear immigration without travel documents. This reduces waiting while maintaining strict security standards.
Beyond transport, speed gates appear in stadiums, government offices, and hospitals. In stadiums, they manage crowds and check tickets. In hospitals, they secure sensitive areas while ensuring smooth staff and patient movement. Their flexibility shows value across many forms of infrastructure.
In essence, speed gates are more than access tools. They are now vital infrastructure shaping safe and efficient urban movement.
Innovation and Future Outlook
The future of speed gates lies at the intersection of AI, data, and sustainability. While today’s systems already enable fast and secure passage, emerging innovations are pushing the boundaries of what speed gates can achieve.:
AI and Intelligent Security:Modern speed gates are no longer limited to verifying credentials. With AI-powered behavioral analysis, they can detect risks such as tailgating or unusual crowd patterns. In smart city projects, gates are increasingly integrated with surveillance platforms, transforming them into intelligent checkpoints that enable proactive threat detection.
Data and Operational Efficiency:Every passage through a gate generates valuable traffic data. By analyzing entry counts, peak hours, and usage trends, facility managers and city planners can optimize staffing, improve building design, and forecast future needs. For example, universities and corporate campuses already rely on such insights to streamline visitor management and enhance workplace efficiency.
Sustainability and Green Design:Manufacturers are adopting energy-efficient motors, recyclable materials, and low-power standby modes to align with green building standards like LEED and BREEAM. This reflects the growing importance of eco-friendly infrastructure that enhances security without compromising environmental responsibility.
Toward Multi-Functional Smart Infrastructure:Looking ahead, speed gates will evolve into multi-functional nodes, combining security, analytics, energy management, and even digital services such as advertising, wayfinding, or real-time notifications. This convergence will transform them from simple access barriers into interactive, intelligent elements of the built environment.
Conclusion
Speed gates are no longer just mechanical barriers; they have become a vital element of modern infrastructure where security, efficiency, and user experience converge. From biometric access in corporate lobbies to data-driven crowd management in metro systems, they demonstrate how access control can be both seamless and intelligent. As innovation continues to push the boundaries—with AI, sustainability, and multifunctional integration leading the way—speed gates are set to play an even greater role in shaping how people move through and interact with urban spaces. Ultimately, they embody the vision of access control that is not only secure, but also smart, sustainable, and human-centered.